Eczema: this annoying and unpleasant skin disease can interfere with our daily activities, endanger our social life and prevent us from getting a good night’s sleep.
WHAT IS ECZEMA?
What exactly is eczema? It is our skin’s reaction to something that irritates it. Just as some people are prone to colds and respiratory system irritation, some are prone to skin irritation. Situations in which these two are connected are not rare. It all boils down to how resistant our body is, its immunity or the lack of it. As eczema is more common in industrial areas, it is obvious that it is most often caused by chemical substances, although today we are surrounded by chemicals to such an extent that even residents of rural areas are not spared.
Strong soaps, detergents, disinfectants, shampoos, perfumes, cosmetics – all these are things that we use regularly and that can act as allergens – they can cause an immune reaction on the skin. In addition to chemicals, irritants can also be house dust, i.e. dust mites, mould, pet hair, tobacco smoke, chlorine and pollen. Allergens trigger eczema, they do not cause it. When the skin is exposed to allergens and is unable to defend itself, atopic dermatitis occurs, the most common form of eczema. Contact dermatitis is a change on the skin that occurs as a result of direct physical contact with irritating particles that cause a rash; the scalp is not spared either, because seborrheic dermatitis affects the scalp and leads to scaling skin. Scratching can only further aggravate the condition and lead to the breaking of the skin and wounds.
SYMPTOMS AND TYPES
The symptoms of eczema are very unpleasant: it starts as dry skin which then becomes red and sore, very itchy, it thickens, further dries and after a while it starts to crack, peel and hurt. It occurs most often in the folds of the skin, the elbows, below the knees, next to the hair, around the eyes, on the feet and palms of the hands. Acute eczema refers to an eczema rash that has just started and is characterised by redness, while chronic eczema is characterised by flaking, thickening of the skin and is greyish in colour. Eczema is in an acute phase while we are in contact with irritating substances; if we remove them, the skin recovers. When eczema is in a chronic phase, it can lead to scars, blemishes and wounds, and as the protection of the skin barrier is compromised, it becomes characterised by periods of deterioration, especially if we are forced to expose ourselves to certain substances, for example at work.
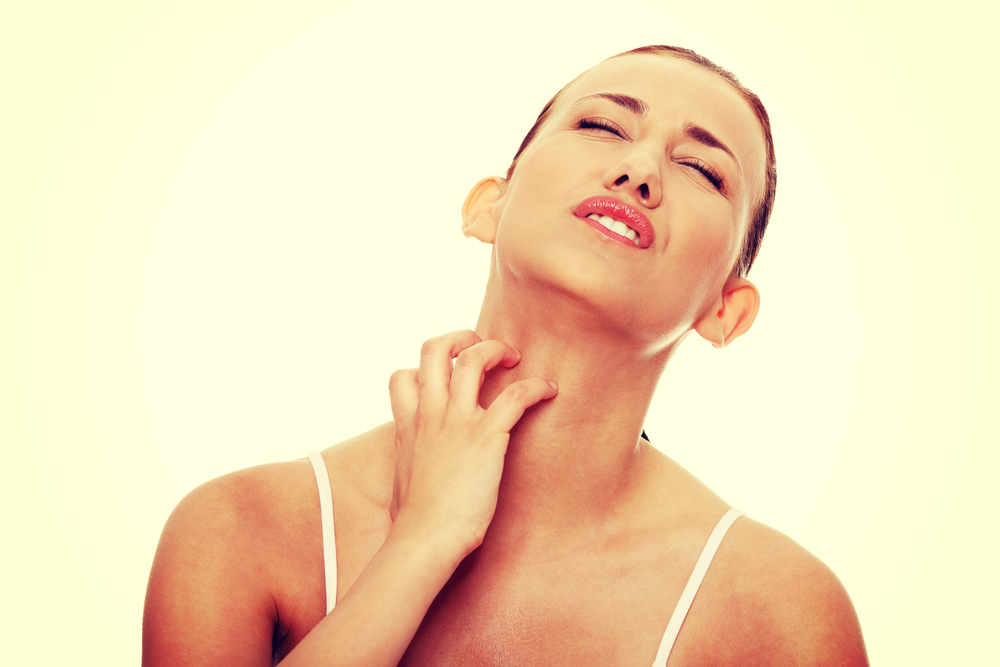

In addition to all this, if purulent blisters also appear, it means that the rash has become complicated and that a bacterial infection has occurred that requires treatment with antibiotics. People with eczema are more likely to get herpes. Although eczema is not contagious, people who visibly suffer from it can experience discomfort and be the subject of social discrimination, or withdraw into themselves, so this condition can also affect a person’s mental well-being.
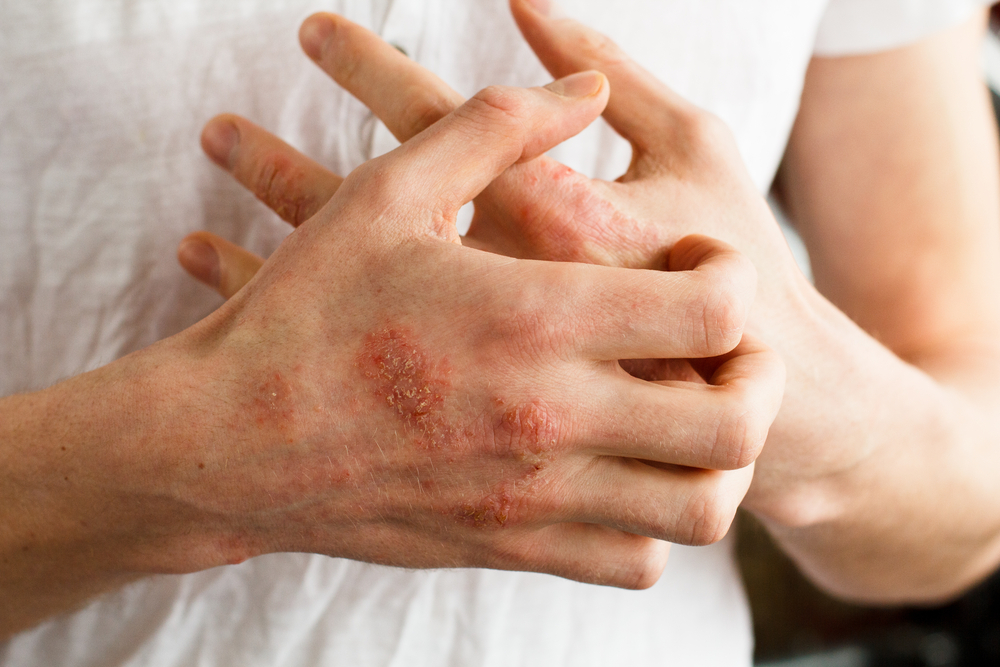
ECZEMA ON HANDS AND FACE
Children’s skin is particularly sensitive and prone to eczema – about 15 percent of children suffer from it. Eczema begins as atopic eczema – dry, itchy and irritated skin, most often on the hands. Dermatitis or hand eczema can occur in early childhood and it can be triggered also by some foods, especially processed foods that contain a lot of additives. Allergens can also be dairy products, soy, eggs, nuts and peanuts, sometimes gluten. Too much unhealthy, fried food and food containing a lot of sugar can make the condition even worse. In children, eczema usually stops by the age of ten, but sometimes it persists and occurs occasionally or frequently for the rest of life. In adults, hand eczema is often an immune reaction to contact with detergents or it can be a consequence of frequent hand washing.
Facial eczema or atopic facial dermatitis can be even more unpleasant, both in the active phase when it is characterised by inflammation and when it subsides, that is, when it is in an inactive phase. Adequate facial care and ointment for eczema in patients with milder forms can calm it down, but in more serious cases more therapy is needed. An additional discomfort of facial eczema is that it is very noticeable, so it can lead to social discomfort and even discrimination, as well as to self-confidence issues and psychological problems.
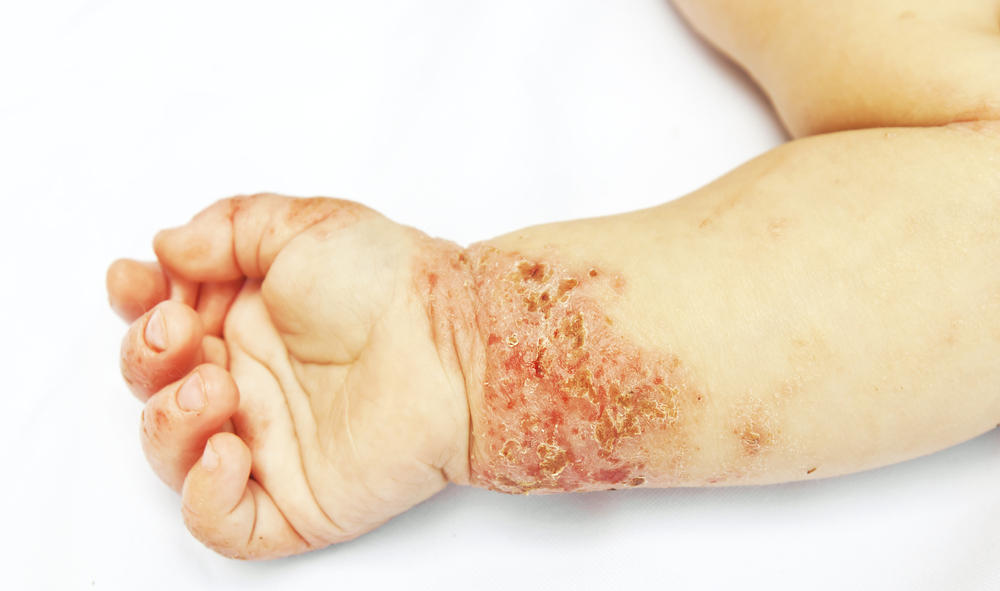
There is no specific medication for eczema that will stop it forever. Corticosteroid ointments can bring temporary relief, however, they have numerous negative effects and can disrupt hormones, so they should be used very carefully, especially for children. It is best to choose natural substances that reduce inflammation, have antibacterial action, promote healing, hydrate, and at the same time do not cause any side effects.
CREAM WITH NATURAL INGREDIENTS
What has nature given us that can result in the retreat of eczema and lead to skin regeneration? The ideal ingredients of an eczema balm are the following:
- Avocado oil has an extremely favourable effect on the skin thanks to its high content of essential fatty acids. It penetrates deep into the skin, regenerates and hydrates it, maintains its elasticity, reduces itching and stimulates collagen metabolism.
- Shea butter protects the skin from inflammation, creates a protective barrier on its surface and is proven to calm the symptoms of eczema.
- Evening primrose oil, rich in fatty acids, promotes skin healing and conditions it, retains moisture and strengthens its immunity.
- Cocoa butter contains fatty acids that have a healing effect on the skin, it calms acute episodes of eczema and additionally protects the skin from the harmful effects of UV rays.
- Jojoba oil calms inflammation and prevents the development and progression of inflammatory processes.
- Wheat germ oil, rich in vitamins and minerals, regenerates and nourishes the skin, protecting it with its strong antioxidant effect.
- Grape seed oil, with its polyphenols and flavonoids, has an antioxidant effect on the skin, improves lipid metabolism and regulates sebum levels.
- Marigold oil is very therapeutic, it acts against infections, rashes, wounds, it tones and moisturises the skin and is very effective for eczema.
- Bisabolol from chamomile kills bacteria, viruses and fungi and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Panthenol regenerates damaged skin, the epidermal cells, and has an extremely hydrating effect.
- Chilean rose oil with its all-trans retinoic acid has been proven to restore the epidermis; it heals, removes spots, scars and wrinkles, while vitamin E in it maintains skin tone.
- Beeswax has antibiotic, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic properties, nourishes the skin, softens and protects it by creating an invisible and light barrier on it surface.
- Broadleaf plantain extract promotes healing by facilitating collagen synthesis.
- Yarrow, a famous healing plant, has a strongly proven anti-inflammatory effect and is therefore the ideal solution for soothing inflammatory rashes in eczema.
- Witch hazel extract has been proven to be effective in the treatment of skin disorders in children, especially eczema, it reduces flaking and itching and strengthens the skin’s immunity.
It is important to know the most optimal proportions for the use of these ingredients – therefore it is best to leave the preparation to experts. All these brilliant ingredients, along with the essential oils of bergamot, rosemary, lavender and mandarin, are an integral part of Devi regeneration balm. This completely natural balm, so mild that it can also be used for children and babies, relieves itching and flaking, soothes inflammation, regulates moisture and completely regenerates the skin.
In addition to being extremely effective as a balm for eczema, it also helps with psoriasis, various kinds of inflammation and skin damage, acne, burns, including those from sun exposure, age spots, wrinkles and scars. It can be used as treatment or simply as prevention and daily skin care for the whole family.

